Education
Bachelors in Electronics and Communication Engineering, Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering, Thapathali Campus, Tribhuvan University, Institute of Engineering.
Publications
- Silent Speech in Nepali
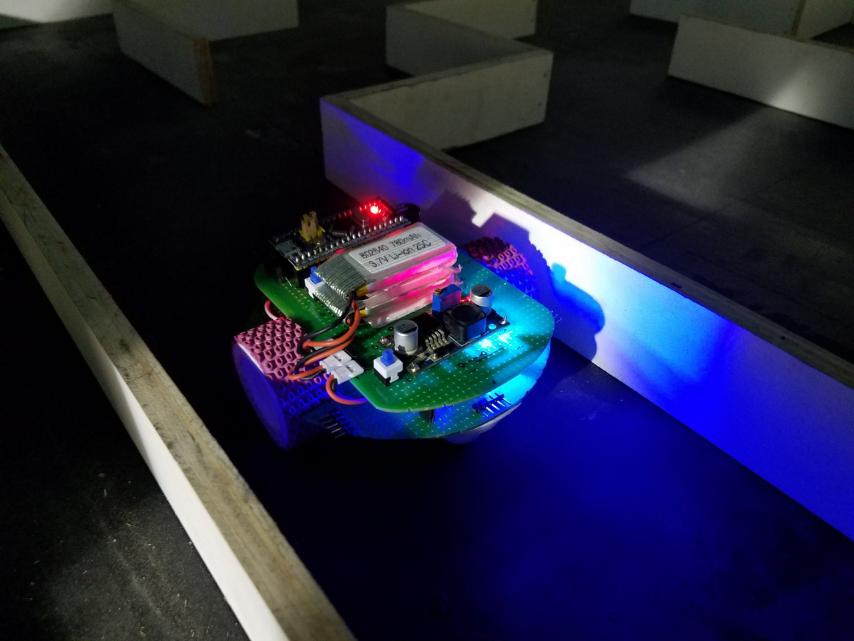
- Optimizing Tremaux Algorithm in Micromouse Using Potential Values
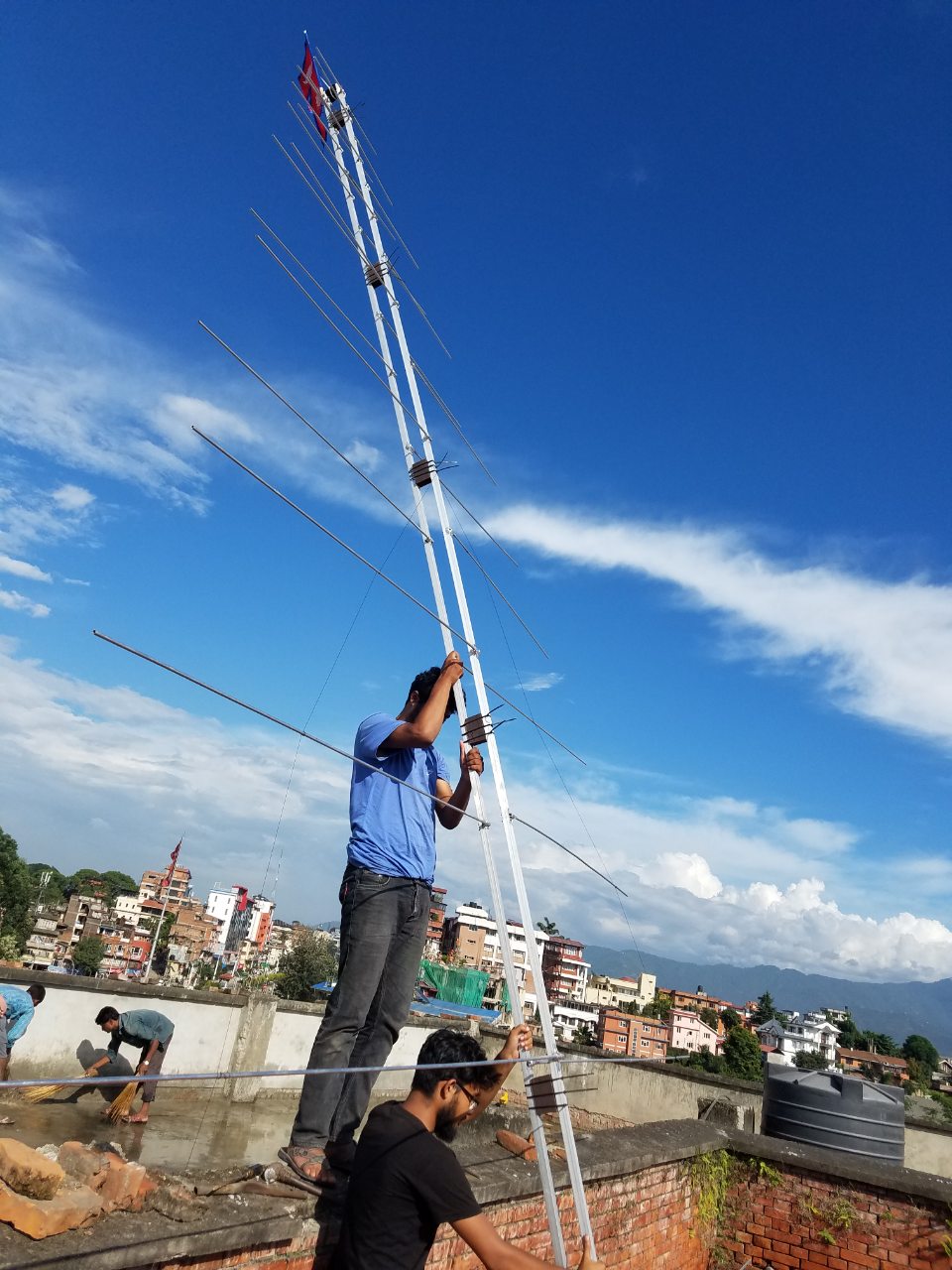
- Design of Log Periodic Dipole Array Antenna Ranging from 30 to 150 MHz
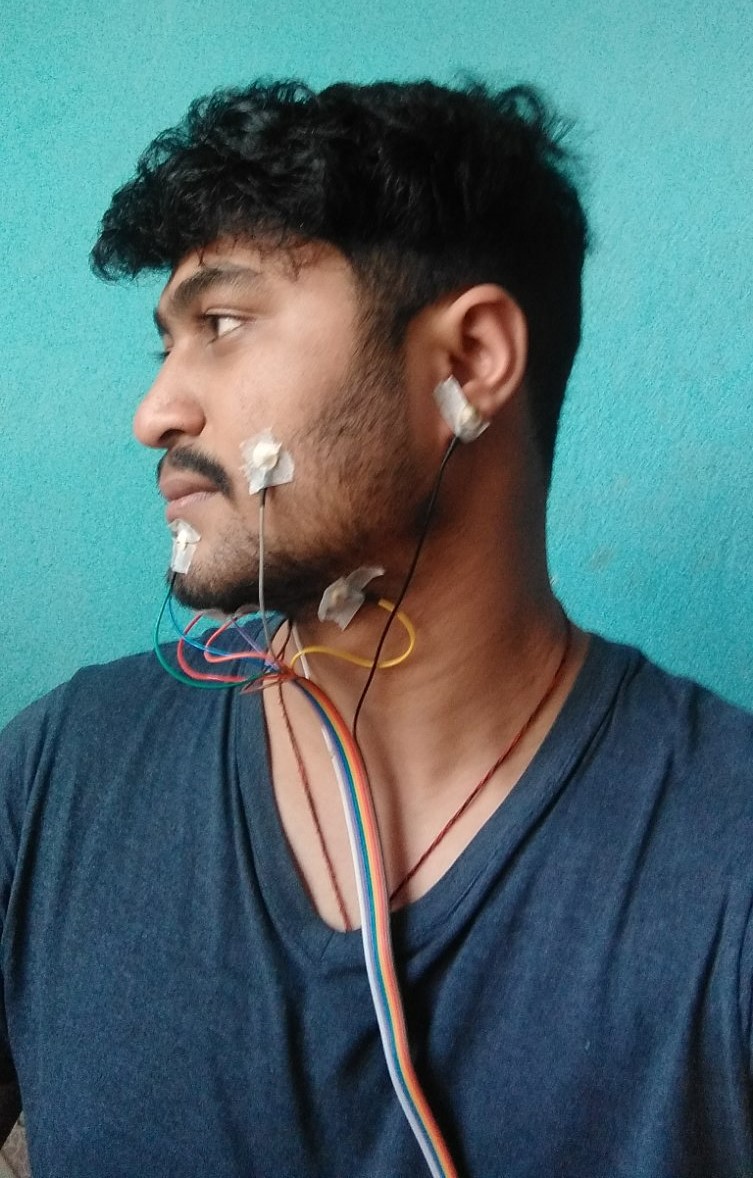
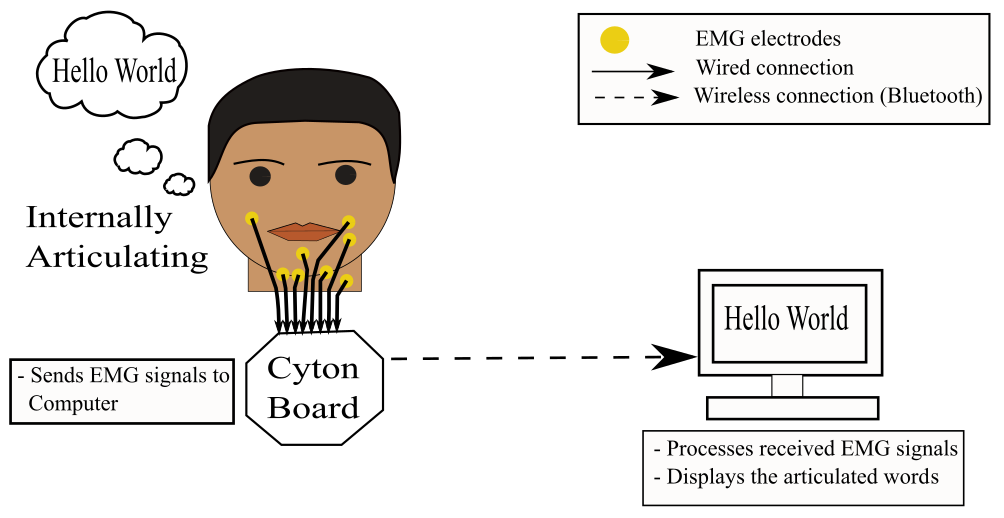
Since the development of the very first computer, human-computer interaction has always required to have some form of physical activity as an input to the computer. Although these methods are accurate and hassle-free, they fail to be intelligible to the differently-abled. Speech interaction tackles this issue to some extent but it is still subjected to privacy issues. The proposed system in this research project confronts these problems and provides a secure and seamless interaction between a human and a computer using silent speech recognition. The surface electromyography (sEMG) signals, during the silent speech, are recorded from the facial muscles of a speaker using 8-channel gold cup electrodes and filtered to remove noise and other unwanted signals. The spectrogram of the processed signal is then extracted to train a Convolution Neural Network (CNN). The trained model is finally deployed to predict the utterances.
Rhimesh Lwagun, Sanjay Rijal, Rabin Nepal, Upendra Subedi, Dinesh Baniya Kshatri
Link to PaperThis paper discusses the furtherance of the Tremaux algorithm by employing a potential value algorithm in conjunction, for improving search in a micromouse. The fused algorithm running on the STM32 Bluepill microcontroller explores and finds the shortest path in a 16x16 maze. Proximity sensors, gyroscope, and magnetometer together with encoder motors aid the micromouse to understand its surrounding hindrances and make precise movements while traversing through a maze. The optimized algorithm eliminates any paths that may lead the micromouse further away from the center of the maze during the initial run itself and saves a significant amount of time while solving a maze
Sanjay Rijal, Rabin Nepal, Rhimesh Lwagun, Rohit Pati, Janardan Bhatta
Link to PaperThis paper describes construction of 16 element frequency independent and high bandwidth Log Periodic Dipole Array antenna which works within the frequency range of 30 to 150 MHz. The antenna of gain 8 dBi is designed by calculating the parameters from Matlab. Matlab program is used to calculate the parameters like length of elements, separation between elements, theoretical impedance, standing wave ratio, etc. Thus, the designed antenna was fabricated. The antenna element is a cylindrical aluminum pipe of diameter 9mm and the boom used is rectangular antenna pipe of dimension 1”X1”. Fabrication also includes other materials like M-seal, zip tie, etc for physical stability of the antenna. Log Periodic Dipole Array antenna design described in this paper is fed with 75 ohm coaxial cable to 1:1 balun. Balun is also used for impedance matching between the antenna and coaxial cable. Antenna analyzer is used to measure Standing Wave Ratio and Impedance which are found to be 1.623 and 71.5625 ohm respectively. The antenna can be a receiver or a transmitter type for operating with the signals within Very High Frequency band.
Upendra Subedi, Rabin Nepal, Rhimesh Lwagun, Sanjay Rijal
Link to Paper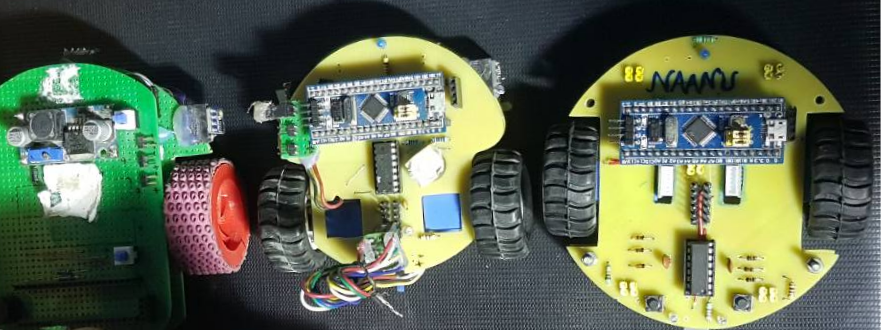
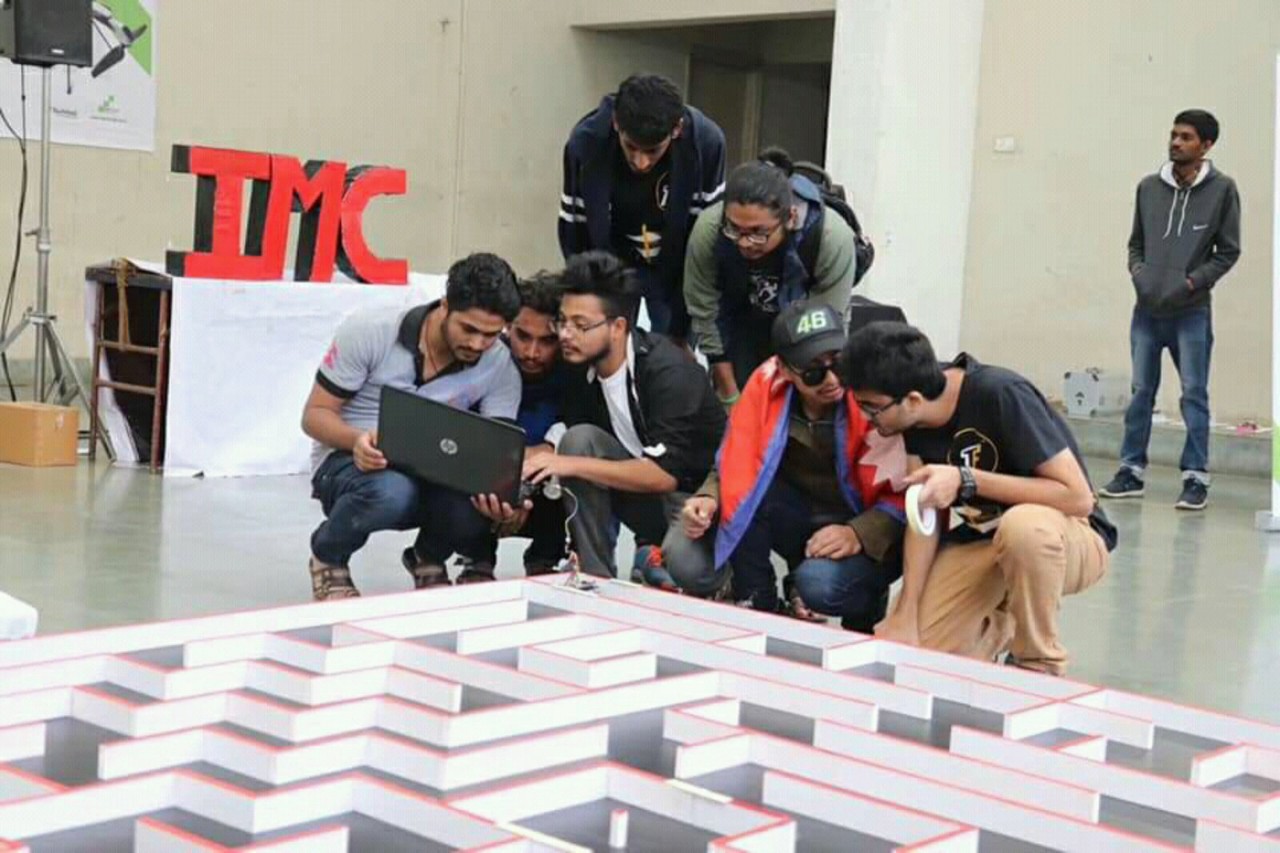
IMC
Micromouse built for the International Micromouse Competition, three versions of the Micromouse built by RAC members.
Human Computer Interface
In this project, internally articulated words are predicted using CNN. The used hardware is OpenBCI which collects the EMG signals from the facial muscles.
Poster Presentation
Secured First Position in the poster presentation competition held in 12th Institute of Engineering Graduate Conference.
Core Member, Robotics and Automation Center
Robotics and Automation Center, an organization by and for students to collabrate on various research and project.